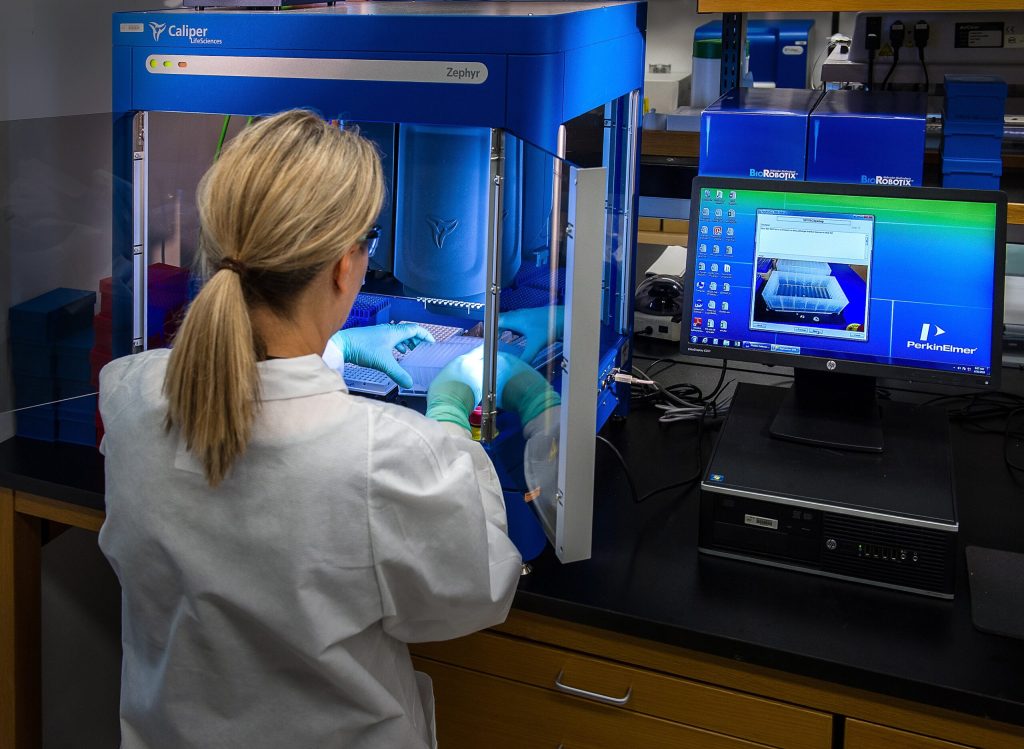
The Saudi healthcare market is expected to generate US$464m in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 12.79% until 2025. Due to its young and growing population, it is estimated that Saudi Arabia will require more than 20,000 additional hospital beds by 2035. Innovations in technology and the global pandemic are amongst the key forces driving changes in Saudi Arabia’s healthcare industry at such an unprecedented rate. From patient care to medical research and training, every aspect of healthcare is being affected by technological advances and operational reforms.
Hospital stays are becoming shorter as more procedures can be carried out on an outpatient basis. This is thanks to advances in diagnostic techniques and treatments, as well as the availability of better-quality medical equipment. Over the coming years, it’s expected that healthcare will become increasingly digitised, improving the level of access and convenience for patients.
The Digitisation Of Healthcare
With the pressure of the global pandemic, Saudi’s healthcare industry has been forced to adapt to new ways of working at a pace that would have been unthinkable just a few years ago. The sudden and rapid increase in patient numbers has necessitated a more consolidated and connected approach to care. In response to this need, the Saudi government has begun working on the development of a unified vision of e-health provision across the Kingdom. It’ll enable patients to access streamlined, efficient, and high-quality care regardless of location.
At the heart of this transformation is the digitisation of healthcare. By making use of new and innovative technologies such as AI, big data, and cloud computing, Saudi Arabia’s healthcare system will be able to become more responsive to the needs of patients. What’s more, these tools will help to improve communication between different care providers, leading to better coordination and delivery of care.
New technologies are already being implemented across the Kingdom’s hospitals. AI is being introduced to interpret patient X-rays, taking some pressure off hospital staff. In the near future, Saudi doctors may be able to mine patient healthcare records using big data technology, to assist with diagnosis and the development of treatment plans. Health tech startups are also playing a crucial role in the digitisation of healthcare in Saudi Arabia.
There are currently 150 health tech startups operating within the Kingdom. One of these is Cura — a locally developed application that allows users to receive remote video consultations with doctors across 34 different specialities. Similarly, a new app named Labayh, gives users the ability to connect with a qualified counsellor or psychotherapist quickly and discreetly. These companies are developing innovative solutions that are making a positive impact on the lives of many patients.
Beyond Saudi Arabia’s borders, Neurosurgeons at John Hopkins performed their first augmented reality surgery in June 2021. VR headsets are also being deployed during medical training, to allow students to practice in a virtual environment before moving on to the real thing. This technology could be used to train the next generation of Saudi doctors, possibly in virtual spaces like the metaverse, to meet the Kingdom’s growing demand for qualified physicians.
How The Legal Industry Is Keeping Up With Development
As the healthcare industry evolves, the legal landscape must keep pace. With the wider proliferation of cloud data storage, the Saudi government introduced a new law that prohibits healthcare providers from storing the personal data of any Saudi national outside the Kingdom. The ongoing push towards Saudization also impacts the Healthcare industry. As it currently stands, each hospital must appoint a locally qualified doctor of Saudi nationality as a medical manager for the hospital, with some exceptions granted for hospitals in very rural or remote locations.
Negligence liability is still an area of Saudi law that does not yet have a well-defined framework. Saudi’s lack of legal precedence means that the results of civil cases are often unpredictable. This presents a challenge for both patients and practitioners when it comes to seeking damages for medical negligence. Most cases are resolved on the principle that a contract between two parties constitutes the law between two parties — unless it is in breach of some element of Shari’ah.
The way technology is impacting the healthcare industry is set to continue at an ever-increasing pace. As more countries around the world begin to adopt similar approaches, the potential for further improvement and efficiency is huge. For Saudi Arabia, the next few years will be crucial in shaping the country’s healthcare landscape for the future.